Address
Road no. 4, Vatara, Notun Bazar
Dhaka, Bangladesh
Address
Road no. 4, Vatara, Notun Bazar
Dhaka, Bangladesh
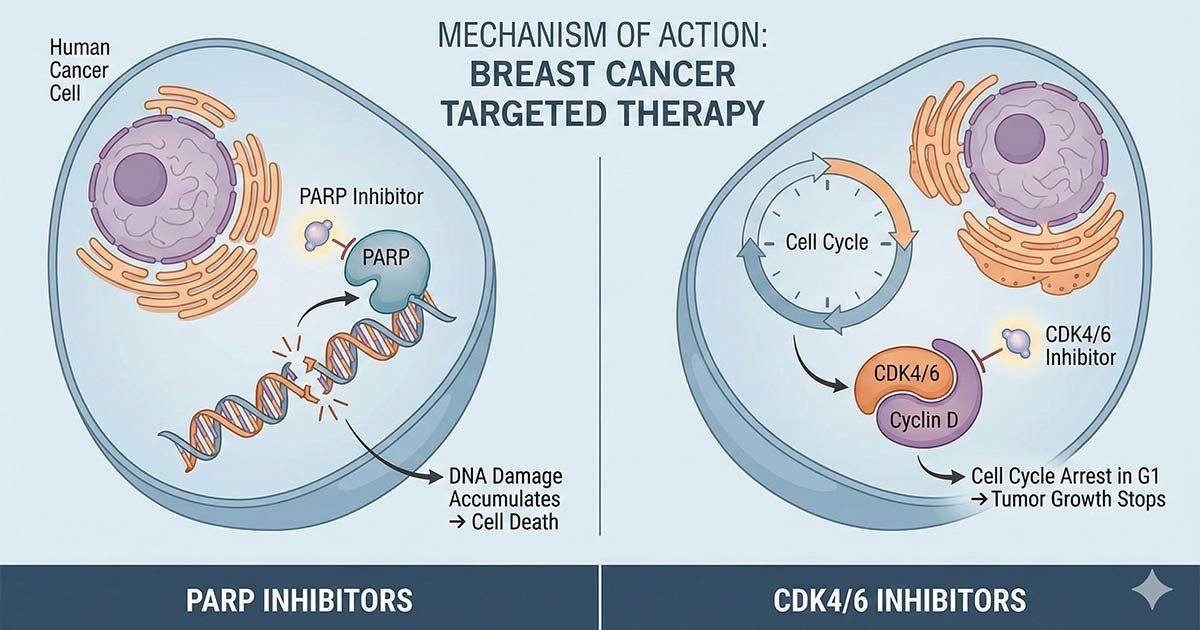
Targeted therapy for breast cancer treatment has undergone a revolutionary transformation in the last two decades. Gone are the days when chemotherapy and radiation were the only lines of defense. Today, the emergence of targeted therapies has changed the landscape for patients, offering personalized treatment options that attack specific cancer cells while sparing healthy tissue.
For patients navigating a diagnosis of metastatic or advanced breast cancer, understanding these options is crucial. Whether it involves hormone receptor-positive (HR+) cancers, HER2-positive types, or those with BRCA mutations, modern medicine provides potent tools to manage the disease and extend quality of life. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the major classes of targeted therapies available today, including CDK4/6 inhibitors, PARP inhibitors, and tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
Unlike chemotherapy, which attacks all rapidly dividing cells, targeted therapy works by interfering with specific molecules involved in the growth, progression, and spread of cancer. By blocking these signals, these drugs can stop cancer cells from dividing or destroy them directly.
This precision makes targeted therapy a cornerstone of modern oncology, particularly for:
For women with Hormone Receptor-Positive (HR+), HER2-Negative metastatic breast cancer, CDK4/6 inhibitors have become a standard of care.
How They Work: Cyclin-dependent kinases 4 and 6 (CDK4/6) are proteins that play a key role in cell division. In many breast cancers, these proteins are overactive, causing cells to divide uncontrollably. Inhibitors block these proteins, effectively putting the “brake” on the cancer cell cycle.
Key Medication: Palbociclib. Palbociclib is one of the most widely prescribed CDK4/6 inhibitors. It is typically taken in combination with hormone therapy (like letrozole or fulvestrant).
Common Side Effects: The most common side effect is neutropenia (low white blood cell count), which is why doctors monitor blood counts regularly. Unlike chemo, it rarely causes hair loss or severe nausea.
For patients with BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene mutations, PARP inhibitors represent a significant breakthrough.
How They Work: PARP is an enzyme that helps repair damaged DNA in cells. Cancer cells with BRCA mutations already have a hard time repairing DNA. When a PARP inhibitor blocks the PARP enzyme, the cancer cells cannot repair themselves at all and die. This concept is known as “synthetic lethality.”
Key Medications:
HER2-positive breast cancer tests positive for a protein called human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2), which promotes cancer cell growth. While monoclonal antibodies (like Trastuzumab) are common, small-molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) are vital for advanced cases, especially when the cancer has spread to the brain.
Key Medications:
The effectiveness of these oral oncolytics depends entirely on adherence—taking the medication exactly as prescribed. However, the high cost of brand-name cancer drugs often becomes a barrier to adherence.
This is where generic oncology medications play a vital role. By providing bioequivalent alternatives to drugs like Palbociclib, Olaparib, and Tucatinib, we ensure that financial toxicity does not prevent a patient from receiving the best possible care. Whether you are prescribed Palbonix, Olanib, or Hertinib, you are receiving a medication designed to meet rigorous standards of efficacy.
A: All three contain the active ingredient Palbociclib. They are manufactured by different pharmaceutical companies but serve the same therapeutic purpose—inhibiting CDK4/6 proteins to treat HR+/HER2- breast cancer. The choice often depends on availability and price, but the clinical effect is intended to be the same.
A: Generally, PARP inhibitors like Olaparib (Olanib/Olarigen) work best in cancers with BRCA mutations or other specific DNA repair defects (HRD). Your oncologist will perform genetic testing to see if these drugs are right for you.
A: Side effects vary by drug. CDK4/6 inhibitors may lower blood counts, while HER2 drugs like Neratinib (Hertinib) can cause diarrhea. It is vital to stay hydrated, keep all doctor appointments for blood work, and communicate any new symptoms to your healthcare team immediately.
A: Yes. Generic versions like Tucaxen or Niranib contain the same active ingredients in the same strength as the branded versions (Tukysa or Zejula). They undergo strict testing to ensure they are bioequivalent.
The era of targeted therapy has brought new hope to the fight against breast cancer. By identifying the specific drivers of a tumor—whether it’s hormonal pathways, HER2 proteins, or DNA repair defects—doctors can prescribe highly effective oral medications that manage the disease for years.
From Palbociclib to Olaparib and Tucatinib, the options are more robust than ever. At Onus Pharma, we are committed to bridging the gap between scientific innovation and patient access, providing a wide range of breast cancer solutions.